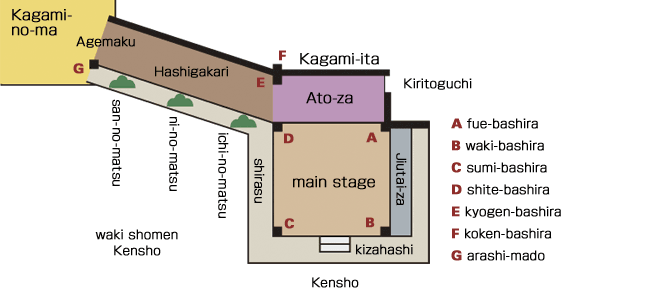
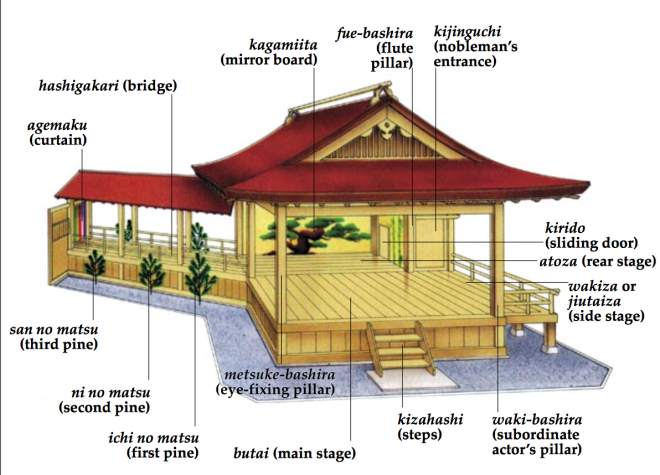
Images
Keychain Theatre Company

World Theatre: 1st December
Prince shotoku: 573-621
- Adopted Chinese culture and Confucianism
- Buddhist sects allowed to develop
Heian Period: 794-1156
- Growth or large, landed esates
- Chinese arts and literature flourish
- Elaborate court life and daily routines
What is Shinto?
- The “sprit Way”
- Ancient, indigenous, mythical, nature religion of japan
- More 1500 years’ old
- No founder – an “ethnic” religion of the Japanese people
The great wave by Hokusai

What is Noh?
- Developed in early 14th Century

- Oldest transmitted performance art in the world
- Integrated popular song and dance from the time period
- Influenced by Buddhism
- Founded by zeami (zay-ahmee)
Noh
- Noh combines elements of dance, drama, music and poetry into one highly aesthetic stage art.
- An art form in which so few elements say so much. Trims off unnecessary details. The ‘Moment’ is important, not the plot.
Simplicity
- Unlike kabuki, Noh is based on simplicity
- No scenery and little if any props are used
- Audience is not separated by a curtain
- Chorus and musicians are onstage
- Instead of pursuing realism, Noh pursues the expression of inner movement through spoken word, music and dance in an extremely simplified space.
Noh
- Most Noh dramas are based on popular classic stories among ordinary people
- Zeami’s stories fall under the style of “Mugen Noh” or “dreamy Noh” where the real world and the dream world cross
Structure of ‘Mugen Noh’
- A traveller visits a place and meets a local person
- The local person tells the traveller about a historic event and story associated wth a person at the locality
- End of story person reveals there a ghost
Characters in Noh
- The protagonist is called “shite” who plays a god, ghost of a samurai or women, madwomen or supernatural characters such a s a goblin or the spirt of a dragon
- The waki is a side character and living person